[비선형 자료구조] 힙
힙(Heap)
-
완전 이진 트리 형태
-
중복 값 허용
-
반 정렬
- 상태부모 노드와 자식 노드의 크기에 대한 우선순위는 보장하지만 형제 노드는 보장X
-
-
최소값 또는 최대값을 빠르게 찾아내는데 유용한 자료 구조
-
최대 힙(Max Heap) : 부모 노드의 키가 자식 노드의 키보다 크거나 같은 형태
-
최소 힙(Min Heap) : 부모 노드의 키가 자식노드의 키보다 작거나 같은 형태
-

힙 삽입
- 트리의 가장 끝 위치에 데이터 삽입
- 부모 노드와 키 비교한 후 작을 경우 부모자리와 교체(반복)

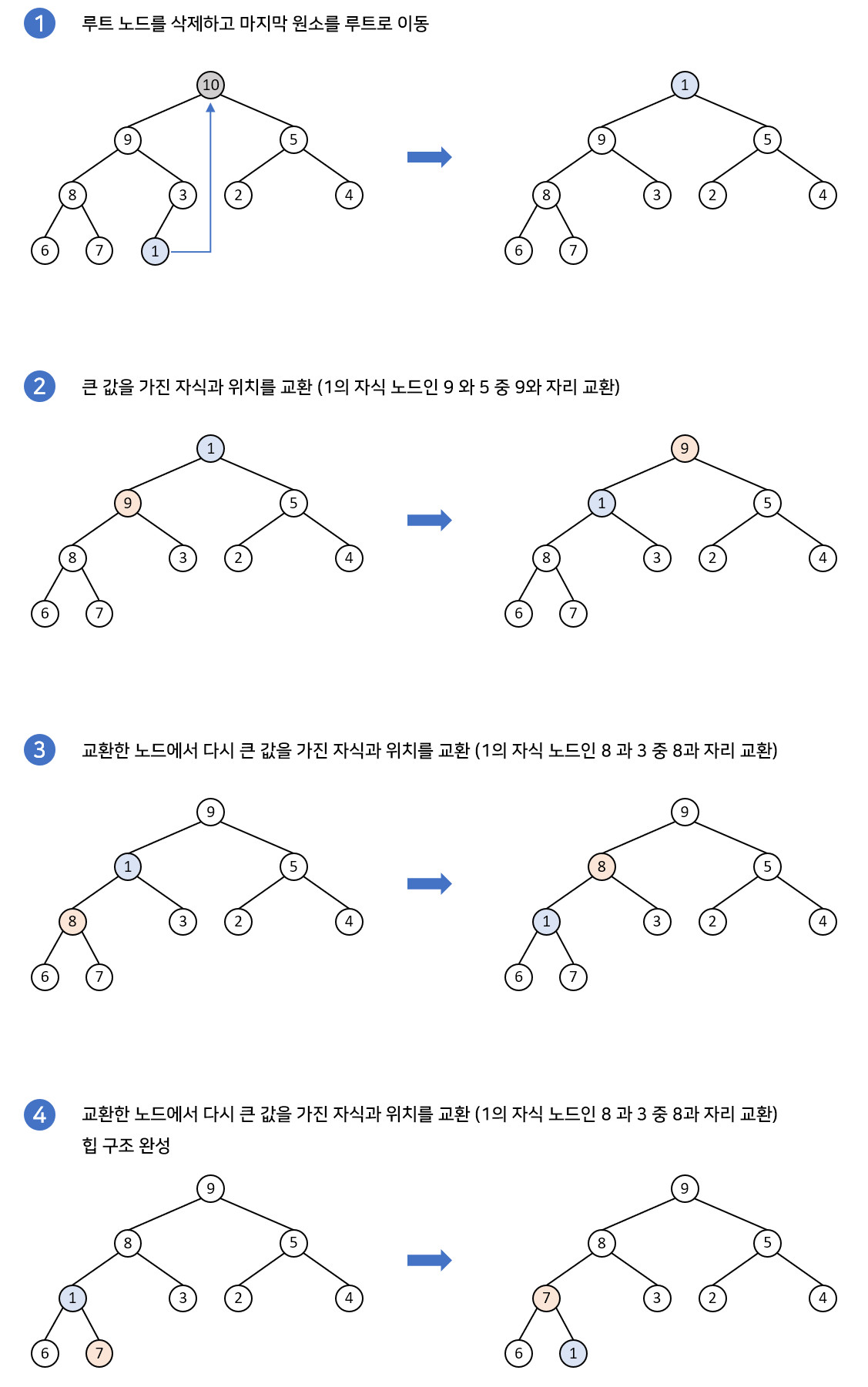
힙 삭제
- 최상위 노드 반환 및 삭제
- 가장 마지막 위치의 노드를 최상위 노드로 위치 시킴
- 자식 노드 중 작은 값과 비교 후 부모 노드가 더 크면 자리 교체(반복)
힙 구현
- Min Heap과 Max Heap 은 부등호 수정으로 간단하게 변경할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Heap {
ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public Heap() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(0); //더미데이터를 추가하여 1번부터 시작할 수있게 설정
}
public void insert(int data) {
heap.add(data);
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
//Min Heap일경우
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) > heap.get(cur)) {
//Max Heap일 경우
//while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) < heap.get(cur)) {
int parentValue = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, data);
heap.set(cur, parentValue);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public Integer delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty");
return null;
}
int target = heap.get(1);
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int cur = 1;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) { //자식 노드가 둘다 있는 경우
//Min Heap일 경우
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) < heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
//Max Heap일 경우
//targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) > heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) { ///자식 노드가 하나 있는 경우
targetIdx = leftIdx;
} else { //부모노드만 있거나 리프노드일 경우
break;
}
//Min Heap일 경우
if (heap.get(cur) < heap.get(targetIdx)) {
//Max Heap일 경우
//if (heap.get(cur) > heap.get(targetIdx)) {
break;
} else {
int parentValue = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentValue);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
return target;
}
public void printTree() {
for (int i = 1; i < this.heap.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.heap.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}

댓글남기기