[알고리즘] 최단 경로
최단 경로(Shortest Path)
- 가중 그래프 상의 두 노드를 연결하는 가장 짧은 경로를 찾는 방법
- 지도 경로 탐색, 네트워크 구축에 드는 비용을 최소화 하는데 사용
- 최단경로 알고리즘
- 다익스트라
- 벨만-포드
- 플로이드-워셜
다익스트라(Dijkstra)
- 출발점에서 목표점까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 한 노드에서 다른 모든 노드로의 최단 경로를 구할 수 있음
- 간선에 음의 가중치가 없어야 함
- 그리디 + DP형태
- 알고리즘 복잡도: O(ElogV) / E :간선수 , V: 노드 수
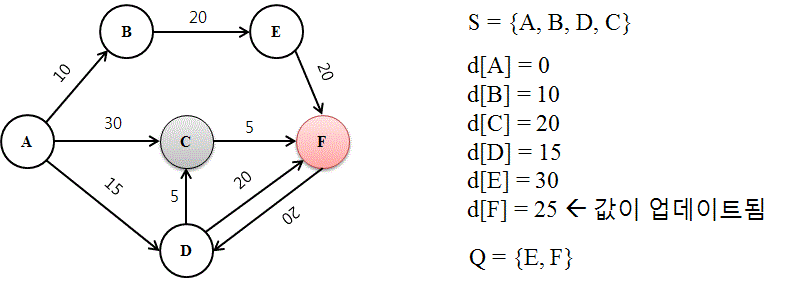
다익스트라 알고리즘 Flow
- 아직 확인하지 않은 거리는 초기값을 Infinity로 설정
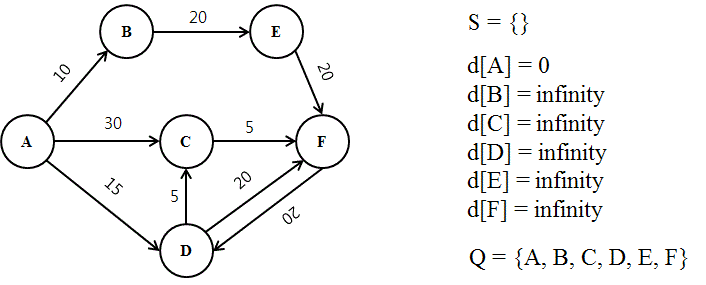
- 루프를 돌려 이웃 노드를 방문 후 거리를 계산
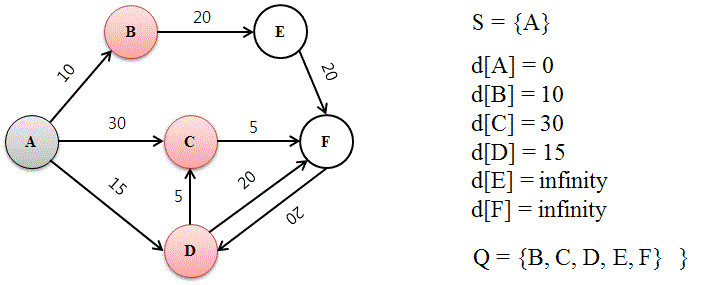
- 최소 경로를 기준으로 다음 목적지 갱신
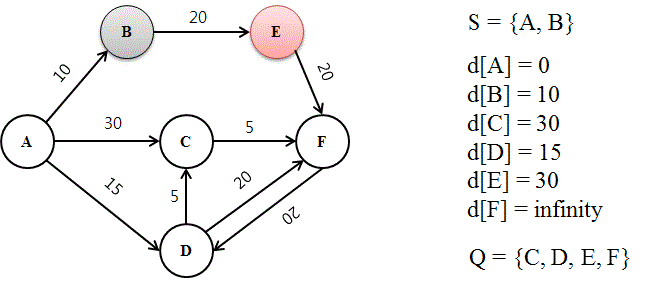
- 새로운 경로가 기존 경로보다 최단 경로 인 경우 값을 업데이트
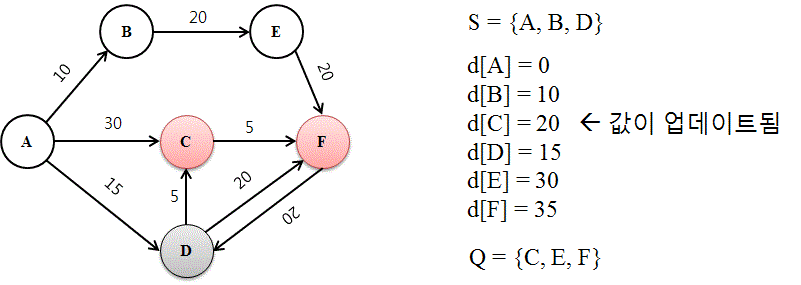
- 또 다른 루프상황
다익스트라 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
public class Dijkstra {
static class Node {
int to;
int weight;
public Node(int to, int weight) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public static void dijkstra(int v, int[][] data, int start) {
// 그래프 생성
ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < v + 1; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
graph.get(data[i][0]).add(new Node(data[i][1], data[i][2]));
}
// DP배열 생성 및 다익스트라 구현
int[] dist = new int[v + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < v + 1; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
dist[start] = 0;
//우선순위 큐 이용
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.weight - y.weight);
pq.offer(new Node(start, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node curNode = pq.poll();
if (dist[curNode.to] < curNode.weight) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(curNode.to).size(); i++) {
Node adjNode = graph.get(curNode.to).get(i);
if (dist[adjNode.to] > curNode.weight + adjNode.weight) {
dist[adjNode.to] = curNode.weight + adjNode.weight;
pq.offer(new Node(adjNode.to, dist[adjNode.to]));
}
}
}
// 데이터 출력
for (int i = 1; i < v + 1; i++) {
if (dist[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.print("INF ");
} else {
System.out.print(dist[i] + " ");
}
}
}
}
벨만-포드(Bellman-Ford)
- 음수 간선이 포함되어 있어도 최단 경로를 구할 수 있음
- 음수 사이클이 있으면 정상 동작하지 않음
- 매번 모든 간선을 확인하기 때문에 다익스트라에 비해 느림
- 알고리즘 복잡도: O(VE) / E :간선수 , V: 노드 수
벨만-포드 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public class BellmanFord {
static class Edge {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public static void bellmanFord(int v, int e, int[][] data, int start) {
Edge[] edge = new Edge[e];
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
edge[i] = new Edge(data[i][0], data[i][1], data[i][2]);
}
int[] dist = new int[v + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < v + 1; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
dist[start] = 0;
boolean isMinusCycle = false;
for (int i = 0; i < v + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < e; j++) {
Edge cur = edge[j];
if (dist[cur.from] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
continue;
}
if (dist[cur.to] > dist[cur.from] + cur.weight) {
dist[cur.to] = dist[cur.from] + cur.weight;
if (i == v) {
isMinusCycle = true;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("음수 사이클 발생 : " + isMinusCycle);
for (int i = 1; i < v + 1; i++) {
if (dist[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.print("INF ");
} else {
System.out.print(dist[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
플로이드-워셜(Floyd-Warshall)
- 모든 노드 간의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 음의 간선이 포함되어 있어도 사용 가능
- 음수 사이클이 있으면 정상 동작 하지 않음
- 알고리즘 복잡도: O(V3)

댓글남기기