[알고리즘] 그리디
그리디(Greedy)
- 매 순간 현재 기준으로 최선의 답을 선택해 나가는 기법
- 빠르게 근사치를 계산할 수 있습니다.
- 결과적으로 최적해가 아닐 수도 있습니다.
그리디 알고리즘 예시
-
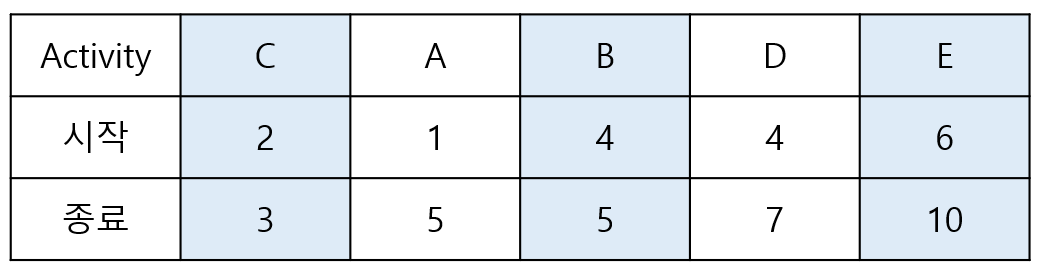
Activity Selection Problem
- N개의 활동과 각 활동의 시작 / 종료 시간이 주어졌을 때 한 사람이 최대한 많이 할 수 있는 활동의 수 구하기
- 종료 시간 기준으로 정렬
- 먼저 종료되는 활동 순, 겹치지 않는 순으로 선택
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class Activity {
String name;
int start;
int end;
public Activity(String name, int start, int end) {
this.name = name;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void selectActivity(ArrayList<Activity> list) {
Collections.sort(list, (x1, x2) -> x1.end - x2.end);
int curTime = 0;
ArrayList<Activity> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Activity item : list) {
if (curTime <= item.start) {
curTime = item.end;
result.add(item);
}
}
for(Activity item : result){
System.out.print(item.name + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
ArrayList<Activity> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Activity("A", 1, 5));
list.add(new Activity("B", 4, 5));
list.add(new Activity("C", 2, 3));
list.add(new Activity("D", 4, 7));
list.add(new Activity("E", 6, 10));
selectActivity(list);
}
}
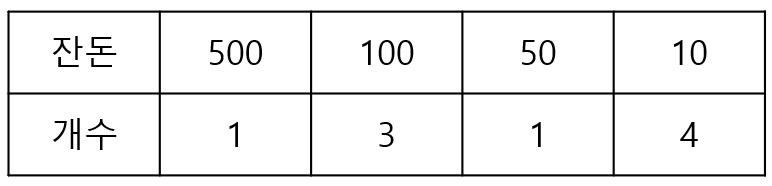
- 거스름돈(동전의 개수 가장 적게)
- 잔돈 890 , 동전 종류 : 10, 50, 100, 500
- 큰 동전부터 계산
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class Main {
public static void getChangeCoins(int receivedMoney, int price) {
final int[] coins = {500, 100, 50, 10, 5, 1};
HashMap<Integer, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
int change = receivedMoney - price;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
if (change < coins[i]) {
continue;
}
int q = change / coins[i];
result.put(coins[i], result.getOrDefault(coins[i], 0) + q);
change %= coins[i];
cnt += q;
}
System.out.println("거스름돈 동전 개수 : " + cnt);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> cur : result.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(cur.getKey() + " : "+cur.getValue());
}
}
}
그리디 알고리즘 적용 조건
- 그리디 알고리즘은 빠르지만 최적해를 보장하지는 못함
- 거스름돈 예제의 경우 [잔돈 890 , 동전 종류 : 10, 50, 400, 500] 최적해가 나오지 않을 수도 있음
- 하기 두 가지 조건에 해당하는 경우 적용 가능
- 탐욕적 선택 특성(Greedy choice property)
- 지금 선택이 다음 선택에 영양을 주지 않음
- 최적 부분 구조(Optimal substructure)
- 전체 문제의 최적해는 부분 문제의 최적해로 이루어짐
- 탐욕적 선택 특성(Greedy choice property)
연습 문제
-
Q1) 정수형 nums 배열이 주어졌다.
각 원소의 값은 해당 위치에서 오른쪽으로 이동할 수 있는 최대 값이다.
첫 번째 위치에서 시작해서 가장 끝까지 이동이 가능한지 판별하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
이동이 가능하면 true, 불가능하면 false 를 반환하세요.
[입출력 예시]
nums: [2, 3, 0, 1, 4] / 출력: true
nums: [3, 0, 0, 1, 1] / 출력: true
nums: [3, 2, 1, 0, 4] / 출력: false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Practice1 {
public static boolean solution(int[] nums) {
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (pos < i) {
return false;
} else if (pos >= nums.length - 1) {
return true;
}
pos = Math.max(pos, i + nums[i]);
}
return true;
}
}
-
Q2) 양의 정수 배열 prices 가 주어졌다.
각 원소의 의미는 주식 가격을 의미한다.
한 번에 한 주만 보유할 수 있다고 할 때 prices 를 보고 사고 팔기를 반복해서 얻을 수 있는 최대 수익을 반환하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
[입출력 예시]
prices: [5, 1, 6, 4, 3, 5] / 출력: 7
prices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 / 출력: 4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Practice2 {
public static int solution(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
profit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
}
return profit;
}
}
- Q3) 양의 정수 n 이 주어지고 다음의 연산을 수행할 수 있을 때 주어진 n 이 1 이 되는데 필요한 최소한의 연산 횟수를 반환하세요.
- n 이 짝수인 경우, 2로 나누기 연산
- n 이 홀수일 때는 1 을 더하거나 1을 빼는 연산
[입출력 예시]
n: 8 / 출력: 3
n: 7 / 출력: 4
n: 9 / 출력: 4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class Practice3 {
public static int solution(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
}
int cnt = 0;
while (n != 1) {
if (n == 3) {
cnt += 2;
break;
}
if (n % 2 == 0) {
n /= 2;
} else if ((n + 1) % 4 == 0) {
n += 1;
} else if ((n - 1) % 4 == 0) {
n -= 1;
}
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
}
-
Q4) 원형 루트 상에 n 개의 주유소가 있다.
각 주유소의 가스 보유량은 gas 배열에 주어지고 해당 주유소에서 다음 주유소로의 이동 비용은 cost 배열에 주어진다.
어떤 위치에서 차량이 가스를 채워 출발하면 모든 주유소를 방문하고 원래의 위치로 돌아올 수 있는지 계산하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
[입출력 예시]
gas: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] / cost: [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] / 출력: 3
gas: [2, 3, 4] / cost: [3, 4, 3] / 출력: -1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class Practice4 {
public static int solution(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
if (gas == null || cost == null) {
return -1;
}
if (gas.length != cost.length) {
return -1;
}
int curGas = 0;
int totalGas = 0;
int startPos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
curGas += gas[i] - cost[i];
totalGas += gas[i] - cost[i];
if (curGas < 0) {
startPos = i + 1;
curGas = 0;
}
}
return totalGas >= 0 ? startPos : -1;
}
}
-
Q5) 정수 num 이 주어졌을 때 num 숫자에서 두 자리를 최대 한번만 교체하여 얻을 수 있는 최대값을 출력하세요.
[입출력 예시]
num: 2736 / 출력: 7236
num: 7116 / 출력: 7611
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class Practice5 {
public static int solution(int num) {
char[] cArr = String.valueOf(num).toCharArray();
int[] maxArr = new int[cArr.length];
int max = 0;
for (int i = cArr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
max = Math.max(max, cArr[i] - '0');
maxArr[i] = max;
}
for (int i = 0; i < cArr.length - 1; i++) {
if (cArr[i] - '0' < maxArr[i + 1]) {
for (int j = cArr.length - 1; j >= 1 + 1; j--) {
if (cArr[j] - '0' == maxArr[i + 1]) {
char tmp = cArr[j];
cArr[j] = cArr[i];
cArr[i] = tmp;
return Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(cArr));
}
}
}
}
return num;
}
}

댓글남기기